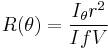Rayleigh ratio
The Rayleigh ratio is a quantity used to characterize the scattered intensity as a function of scattering angle  , and is defined as
, and is defined as
where 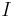 is the intensity of the incident radiation,
is the intensity of the incident radiation, 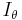 is the total intensity of scattered radiation observed at an angle
is the total intensity of scattered radiation observed at an angle 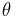 and a distance
and a distance 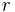 from the point of scattering and
from the point of scattering and 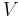 is the scattering volume. The factor
is the scattering volume. The factor  is introduced to compensate for polarization phenomena, and is dependent of the type of radiation used as follows:
is introduced to compensate for polarization phenomena, and is dependent of the type of radiation used as follows:
1. For light scattering,  depends on the polarization of the incident beam, and is
depends on the polarization of the incident beam, and is 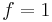 for vertically polarized light,
for vertically polarized light, 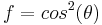 for horizontally polarized light and
for horizontally polarized light and 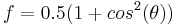 for unpolarized light.
for unpolarized light.
2. For small-angle neutron scattering, 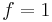 .
.
3. For small-angle X-ray scattering, 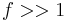 , if
, if 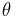 < ~ 5° .
< ~ 5° .
Notes:
1. The dimension of 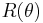 is an inverse length.
is an inverse length.
2. In small-angle neutron scattering the term cross-section is frequently used in place of 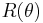 .
.
3. IUPAC also recommends the symbol 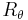 .
.